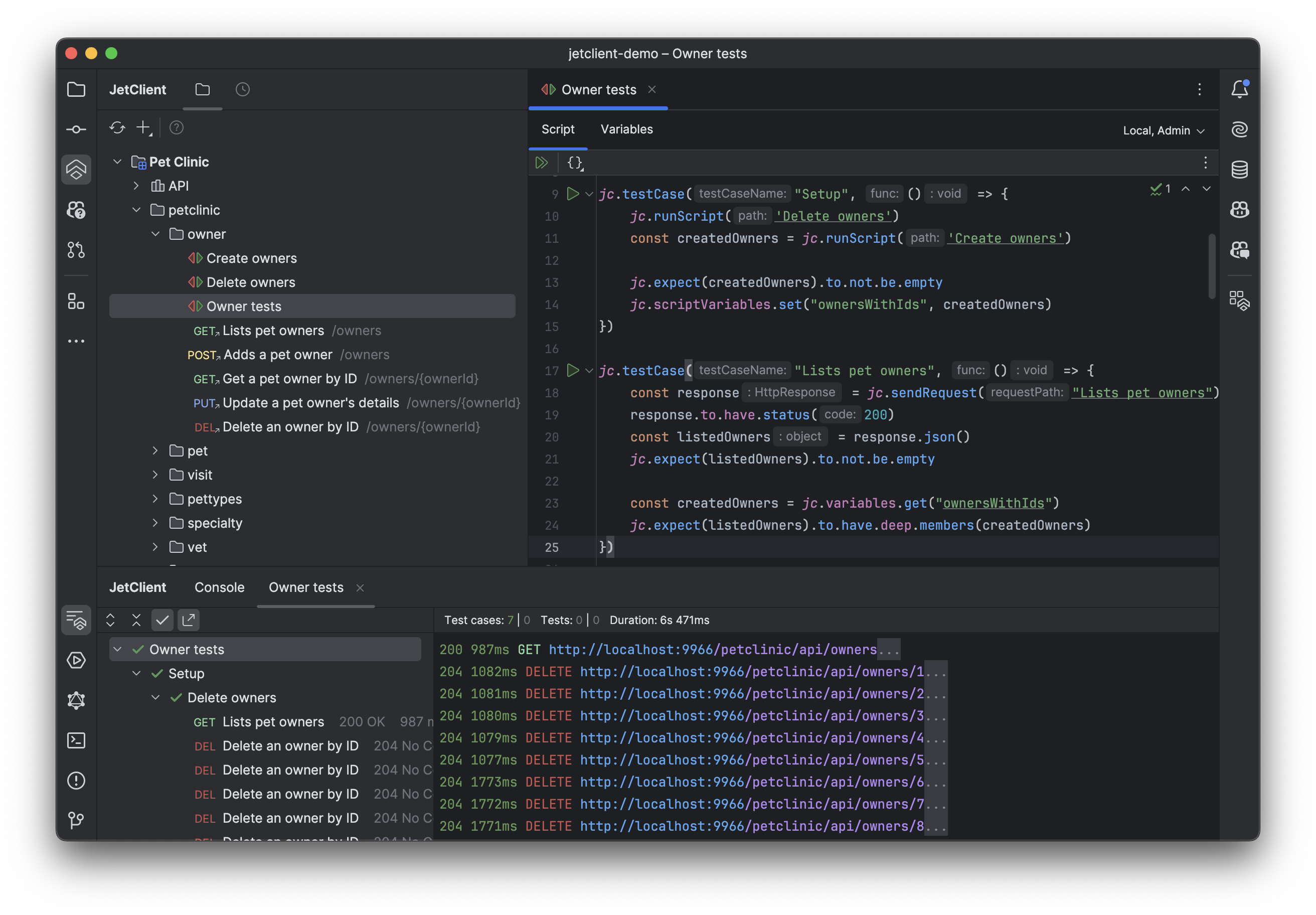
Write Tests
JetClient provides a built-in testing framework that uses Chai.js assertions to validate API responses. You can write tests using jc.test and create test cases using jc.testCase in any script. Test cases are particularly useful in standalone scripts where they can be executed independently using the Run button in the editor gutter.
Basic Tests
Use jc.test to define a test. A test fails if an error is thrown inside the function:
jc.test("Status test", () => {
jc.response.to.have.status(200)
})
jc.test("Response validation", () => {
jc.response.to.not.be.error
jc.response.to.have.jsonBody()
jc.response.to.not.have.jsonBody("error")
})Test Cases
Use jc.testCase in standalone scripts to create executable test cases. When defined, a Run button appears in the editor gutter for independent execution:
jc.testCase("User API Tests", () => {
// Multiple test functions
jc.test("Status should be OK", () => {
jc.response.to.have.status(200)
})
jc.test("Response should have user data", () => {
jc.response.to.have.jsonBody("id")
jc.response.to.have.jsonBody("name")
})
})Test cases can also contain direct assertions:
jc.testCase("Authentication Test", () => {
// Send login request with modifications
const response = jc.sendRequest('/myCollection/myFolder/myRequest', (request) => {
request.setBodyJson({ username: "test", password: "test" })
})
// Validate response
response.to.have.status(200)
response.to.have.jsonBody("token")
})Response Assertions
Status Code Assertions
// Basic status assertions
jc.response.to.be.ok // Status 200
jc.response.to.have.status(201) // Specific status
// Status category assertions
jc.response.to.be.success // 2xx status
jc.response.to.be.clientError // 4xx status
jc.response.to.be.serverError // 5xx status
jc.response.to.be.error // 4xx or 5xx status
// Common status assertions
jc.response.to.be.unauthorized // Status 401
jc.response.to.be.forbidden // Status 403
jc.response.to.be.notFound // Status 404
Header Assertions
// Check header existence
jc.response.to.have.header("Content-Type")
// Check header value
jc.response.to.have.header("Content-Type", "application/json")Body Assertions
// Check body existence
jc.response.to.have.body()
// JSON body checks
jc.response.to.have.jsonBody()
jc.response.to.have.jsonBody("user.id", 123)Complex Assertions
jc.test("Complex response validation", () => {
const body = jc.response.json()
// Array assertions
jc.expect(body.items).to.be.an("array").that.has.lengthOf(3)
// Property assertions
jc.expect(body).to.have.property("timestamp")
.that.matches(/^\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}/)
// Value assertions
jc.expect(body.count).to.be.a("number")
.that.is.within(1, 100)
})Test Failure Handling
A test fails if an error is thrown or an assertion fails. You can explicitly fail a test using:
jc.expect.fail("Test failed: Invalid response format")Async Test Cases
For tests involving asynchronous operations, use jc.testCaseAsync:
// Using promise
jc.testCaseAsync("Async API Test", async () => {
// First request
const response1 = await jc.sendRequestAsync("/folder/request")
response1.to.have.status(200)
// Use data from first response
const userId = response1.json().id
// Second request using data
const response2 = await jc.sendRequestAsync("/folder/request2", (request) => {
request.setQueryParam("userId", userId)
})
response2.to.have.status(200)
}).then(() => {
console.log("Test completed")
}).catch(error => {
console.error("Test failed:", error)
})
// Using await
await jc.testCaseAsync("Async API Test", async () => {
const response = await jc.sendRequestAsync("/folder/request")
response.to.have.status(200)
})For more details on available assertions, refer to the Chai.js BDD API.